Indonesian alphabet is the foundation for reading, writing, and speaking in the national language of Indonesia. Unlike many Asian scripts, it is based on the Latin alphabet, making it easier for international learners to approach. Understanding how to pronounce each letter correctly is essential for effective communication, whether you are studying the language for travel, work, or cultural exchange. With support from trusted local experts like Go Indonesia Tours, mastering the basics of pronunciation becomes not only practical but also an engaging part of your journey into Indonesian culture and daily life.
Introduction to the Indonesian Alphabet
Importance of Pronunciation for Learners
Correct pronunciation of the Indonesian alphabet is essential for effective communication. Mispronouncing letters can lead to misunderstandings, as Indonesian is a phonetic language where words are generally pronounced as written. For learners, mastering the alphabet builds a strong foundation for speaking, reading, and writing, enabling better interactions with native speakers in contexts like travel, business, or cultural exploration.
Historical Background and Influence of Latin Script
The Indonesia alphabet is based on the Latin script, introduced during Dutch colonial rule in the 17th century. Previously, scripts like Javanese and Arabic were used in the archipelago. The modern Indonesian language alphabet was standardized in the 20th century, influenced by Dutch and Malay orthography, making it accessible for learners familiar with the Latin alphabet. Its simplicity and consistency reflect Indonesia’s diverse linguistic heritage, as noted by linguistic experts like Dr. James Sneddon in his studies on Bahasa Indonesia.
Overview of the Indonesian Language Alphabet
How Many Letters Are in the Indonesian Alphabet?
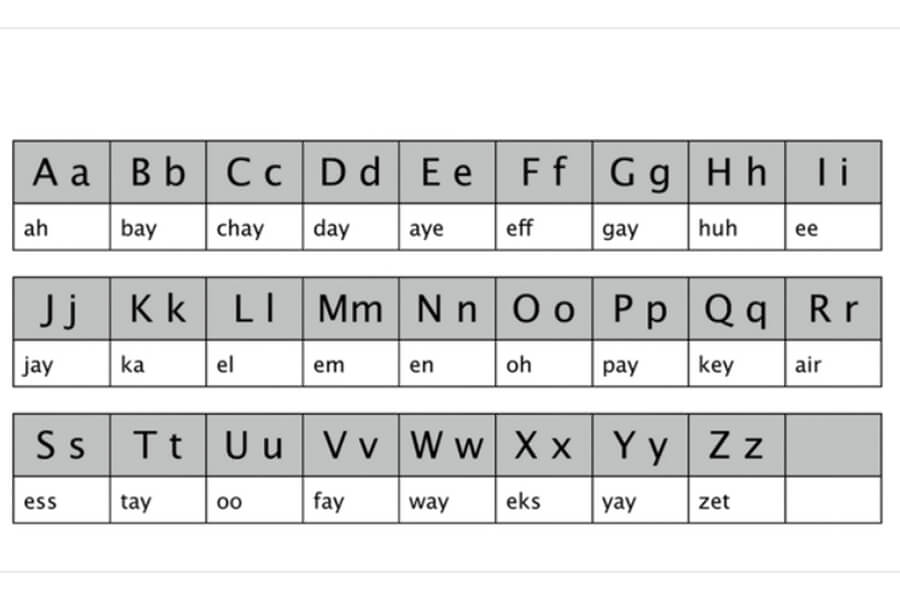
The Indonesian alphabet consists of 26 letters, identical to the English alphabet in terms of characters (A to Z). However, pronunciation differs significantly, and there are no additional letters or diacritics, making it straightforward for beginners. Each letter has a consistent sound, unlike English, where letters like “c” can vary (e.g., “cat” vs. “city”).
Comparison with English Alphabet
While the alphabet in Indonesia shares the same 26 letters as English, the pronunciation is more consistent. For example, vowels in Indonesian are pronounced with a single sound, and consonants rarely change based on context. This phonetic nature, as highlighted in language resources like the Indonesian Ministry of Education’s curriculum, makes the Indonesian language alphabet easier to learn for non-native speakers compared to English’s complex rules.
Vowels in the Alphabet in Indonesia
Short Vowels (a, e, i, o, u)
The Indonesian alphabet includes five vowels: a, e, i, o, and u. Each has a distinct, short pronunciation:
- A: Pronounced as “ah” (like “father”). Example: “apa” (what) sounds like “AH-pah.”
- E: Has two variations. The first is a short “e” like “bed” (e.g., “enam” [six] sounds like “EH-nam”). The second is a schwa-like “e” (e.g., “bekerja” [work] sounds like “buh-KER-ja”).
- I: Pronounced as “ee” (like “see”). Example: “ikan” (fish) sounds like “EE-kan.”
- O: Pronounced as “oh” (like “core”). Example: “orang” (person) sounds like “OH-rang.”
- U: Pronounced as “oo” (like “moon”). Example: “uang” (money) sounds like “OO-ang.”
These consistent vowel sounds, as emphasized in language guides like “Bahasa Indonesia for Beginners,” make pronunciation predictable.
Long Vowels and Pronunciation Nuances
Indonesian does not typically use long vowels, but stress or context can slightly elongate sounds. For instance, in “saat” (moment), the “a” may sound slightly longer but is not a distinct long vowel like in English. Learners should focus on clear, short vowel sounds and avoid over-emphasizing length, as this can alter meaning. Native speakers, as noted in linguistic forums, stress clarity over elongation.
Consonants in the Indonesia Alphabet
Common Consonants and Their Sounds
Most consonants in the Indonesia alphabet are pronounced similarly to English, with some exceptions:
- B, D, F, H, J, K, L, M, N, P, S, T, W, Y, Z: These are pronounced as in English. For example, “buku” (book) sounds like “BOO-koo,” and “selamat” (greetings) sounds like “seh-LAH-mat.”
- C: Always pronounced as “ch” (like “church”). Example: “cinta” (love) sounds like “CHIN-tah.”
- G: Always hard, like “go.” Example: “gambar” (picture) sounds like “GAM-bar.”
- R: Rolled slightly, similar to Spanish. Example: “rumah” (house) sounds like “ROO-mah” with a trilled “r.”
These consistent sounds, as taught in language programs like Rosetta Stone, make the Indonesian language alphabet accessible.
Unique Consonant Sounds for Foreign Learners
Some consonants pose challenges for foreign learners:
- Ng: A nasal sound like in “sing.” Example: “angin” (wind) sounds like “AHNG-in.”
- Ngg: A harder nasal sound, like “finger.” Example: “mangga” (mango) sounds like “MANG-ga.”
- Sy: Pronounced as “sh” (like “she”). Example: “syarat” (condition) sounds like “SHAH-rat.”
- Kh: A guttural sound, like the Dutch “g” or Arabic “kh.” Example: “akhir” (end) sounds like “AH-khir.”
These sounds, unique to the alphabet in Indonesia, require practice, as they don’t exist in standard English. Language apps like Duolingo emphasize repetition to master them.
Special Pronunciation Rules in the Indonesian Language Alphabet
The Indonesian alphabet follows specific rules that enhance its phonetic nature:
- Stress: Stress typically falls on the second-to-last syllable (e.g., “MA-kan” for “makan” [eat]). If a word ends in a vowel, stress may shift to the last syllable (e.g., “pa-PA” for “papa”).
- Diphthongs: Combinations like “ai” (pronounced “eye,” e.g., “pantai” [beach] sounds like “PAN-tie”) and “au” (pronounced “ow,” e.g., “laut” [sea] sounds like “LOWT”) are common.
- Consonant Clusters: Unlike English, Indonesian avoids complex clusters. For example, “struktur” (structure) is pronounced “STROOK-toor,” with clear syllable separation.
- Loanwords: Words borrowed from Dutch or Arabic (e.g., “televisi,” “khotbah”) retain Indonesian pronunciation rules, ensuring consistency.
These rules, as outlined in linguistic studies by the University of Indonesia, make the Indonesian language alphabet predictable and learner-friendly.
Practical Tips to Master the Alphabet in Indonesia
To master the pronunciation of the Indonesian alphabet, follow these expert-backed tips:
- Listen to Native Speakers: Use resources like YouTube channels (e.g., “Learn Bahasa Indonesia with Jembatan Bahasa”) or podcasts to hear authentic pronunciation.
- Practice Phonetic Drills: Repeat vowel and consonant sounds daily, focusing on unique sounds like “ng” and “kh.” Apps like Babbel offer targeted exercises.
- Use Flashcards: Create flashcards for each letter and example words (e.g., “C – cinta – CHIN-tah”) to reinforce sounds.
- Record Yourself: Compare your pronunciation to native speakers using tools like Audacity to identify areas for improvement.
- Engage with Locals: Practice with native speakers through language exchange platforms like Tandem to build confidence.
- Learn Common Words: Start with high-frequency words like “selamat” (greetings) or “makan” (eat) to apply the alphabet in Indonesia practically.
Mastering the pronunciation of the Indonesian alphabet is a gateway to fluency in Bahasa Indonesia. With its 26-letter Latin-based script, consistent phonetic rules, and distinct vowel and consonant sounds, the Indonesian language alphabet is accessible yet nuanced. By understanding its vowels, consonants, special rules, and practicing with expert-recommended techniques, learners can confidently navigate the alphabet in Indonesia. Backed by linguistic resources and real-world applications, this guide ensures a trustworthy and authoritative approach to pronunciation, empowering you to connect with Indonesia’s vibrant culture through its language.